What is Decentralized Finance (DeFi)?
- Real Vision
- September 23, 2022
- 2:19 PM

Did you know that money deposited in a bank is not technically yours after you deposit it? No, neither did we. When depositing money into a bank account you actually become a lender.
We place our faith in financial institutions every single day. Trusted with our savings and our investment accounts, these service providers protect people’s livelihoods. However, due to the centralized nature of the traditional financial system, there is often very little information shared to end-consumers.
However, there is a new financial disruptor approaching, and it is approaching at ‘breakneck speed.’ Thanks to a combination of blockchain technology, smart contracts, and user-supplied liquidity, autonomous financial applications now offer similar financial services without the requirement of a centralized entity. These applications are collectively termed decentralized finance.
Understandably, the idea is a powerful one, however, it can also be a minefield for those interested. So, to help you navigate this innovative financial framework, in this guide, we will aim to define decentralized finance, explain how it works, outline what it can be used for today, and help you determine if it is worth looking into further.
Understand the Future of Everything

Join the Crypto Revolution
Start Your Free Membership Now
100% Free. Yep, You Heard Us
Defining Centralized Finance
To understand decentralized finance, it can be extremely useful to first look at its opposite — centralized finance. Centralized finance encompasses all of the financial products and services that the average consumer is familiar with.
Traditionally, lending, borrowing, and trading are all managed by centralized organizations, such as banks and brokers. These centralized organizations are governed by official bodies and are typically supported by governments. U.S. banks are regulated by the Federal Reserve and the Securities and Exchange Commission. U.K. banks are regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority, and Australian banks are controlled by the Australian Financial Security Authority.
Unfortunately, there is no easy way to access centralized services directly. Access typically involves interacting with a host of intermediaries, handing over important personal information, and requires relinquishing the custody of funds. To rub salt in the financial wound, a percentage of every transaction goes straight to service providers as profit. As a result of the monopoly these organizations have, there is often very little choice. If you want access to financial services, you have to follow the rules of the game.
What Is Decentralized Finance?
Decentralized finance, or DeFi for short, is an umbrella term for a sector of the cryptocurrency industry that focuses on the decentralization and reinvention of traditional financial services. It seeks to remove the intermediaries and join all members of the financial chain through a peer-to-peer network.
According to the CEO and co-founder of DeFi app TrustToken, “DeFi takes the key elements of the work done by banks, exchanges, and insurers today — like lending, borrowing, and trading — and puts it in the hands of the people.”
Most of you will be familiar with Bitcoin, a digital coin that allows for the transfer of wealth. Bitcoin can be transferred across the Bitcoin blockchain without the need for centralized approval from a third party. Drawing inspiration from blockchain technology, decentralized finance takes this one step further.
Instead of limiting the idea to transactions, the sector aims to decentralize products that would otherwise be offered by centralized banks or brokerages.
These decentralized services are packaged into decentralized applications (dApps for short). However, the term dApps can sometimes be slightly misleading. In reality, these applications are simply websites. However, instead of being built and developed on a centralized server such as Google, applications are built and developed on a blockchain.
The first DeFi application was launched in 2017 and offered users the ability to access USD stablecoin loans in return for depositing cryptocurrencies. Since that moment, the DeFi sector has expanded to offer users the ability to borrow, exchange, trade, and save. All services that would traditionally require a centralized provider, can now be accessed through permissionless platforms. In addition to universal access, these platforms allow users to remain the custodian of funds at all times.
Fun Fact: The term DeFi and decentralized finance were first introduced in 2018 by Ethereum developers after the idea of financially focused apps began to take hold. Ethereum remains the key blockchain for DeFi application deployment, however, other Layer-1 blockchains that offer alternative infrastructures are slowly amassing native DeFi ecosystems. The total value locked within DeFi is now spread across blockchains including Ethereum, Tron, Solana, Avalanche, and BNB blockchains.
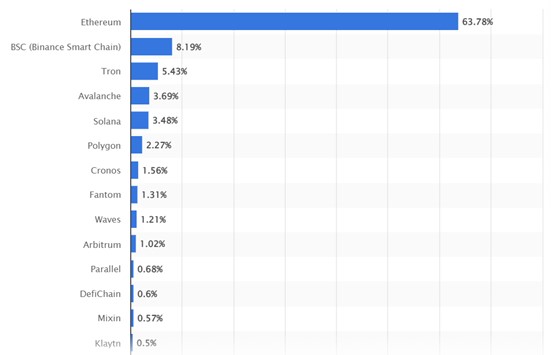
Distribution of total value locked within the DeFi apps of each blockchain.
How Does DeFi Work?
Decentralized finance is complex. There is no doubt about that. However, the operations of DeFi can be broken down into three major contributors: (1) blockchain technology, (2) smart contracts, and (3) user-supplied liquidity.
Blockchain
Blockchains are usually described as decentralized public ledgers. A ledger is simply a place to record data. However, the significance of blockchain ledgers is that these ledgers are updated by a peer-to-peer network. If one participant in the network goes offline, there are thousands of others to keep the blockchain operational. As a result, these systems are transparent, secure, and immutable (can’t be changed). Blockchains are the backbone of DeFi development.
All transactions that take place within a DeFi app are recorded on a blockchain. Transactions are recorded accurately and cannot be tampered with, which is exactly what you need when dealing with financial applications. However, not all blockchains can support DeFi apps. DeFi protocols can only be built on top of blockchains that support smart contracts.
Smart Contracts
In the simplest form, smart contracts are programmable sets of instructions that are executed via a blockchain. Contracts can be created for anything and everything. If a process can be coded, it can become a smart contract.
DeFi apps are composed of thousands of smart contracts, all working in harmony to offer autonomous financial services. The use of smart contracts means that there is no need for human input. DeFi applications can remain operational 24 hours a day, 365 days a year. The first blockchain to offer smart contract functionality was Ethereum. However, since then, several other Layer 1 blockchains have been launched that offer similar capabilities.
User-Supplied Liquidity
The final necessity for the success of DeFi is user-supplied liquidity. In traditional finance, the liquidity required for services is provided by a handful of banks and market makers. Unfortunately, the same liquidity is still required for DeFi services. You need liquidity so that users can take out loans or perform an exchange. So, where does this liquidity come from?
The answer rests with individuals. Every DeFi application is backed by user-supplied liquidity. Anyone is free to deposit cryptocurrencies or stablecoins and support a chosen DeFi application. Just like in traditional finance, in return for supporting a service, liquidity providers are rewarded; the main difference is that in DeFi, most rewards end up with liquidity providers rather than the central platform providing the service.
It is the combination of blockchains, smart contracts, and user-supplied liquidity, that have allowed DeFi apps to thrive. Blockchains ensure that transactional data is recorded and stored in a decentralized manner. Smart contracts ensure that DeFi apps remain operational 24/7 and user-supplied liquidity ensures that all members in a financial chain are directly connected, rather than reliant on communicating through intermediaries.
What Can You Do With DeFi?
When trying to determine what DeFi is, one of the best things to do is to look at what DeFi is used for. Thanks to the ever-expanding list of applications, users can swap, borrow, lend, save, and trade like never before. Below is a list of some innovative use cases within the realm of DeFi:
P2P Lending and Borrowing
Lending and borrowing platforms were some of the first to grace the cryptocurrency sector. Lending protocols allow liquidity providers to deposit funds to earn interest. Likewise, the same protocols then offer liquidity to those looking for loans. Borrowers must deposit other crypto as collateral.
Due to rules such as over-collateralization and small loan-to-value ratios, loans can be accessed instantly and often without the need for traditional credit checks. The amount locked within DeFi lending protocols is referenced by the Total Value Locked (TVL) and peaked at $182 billion in December 2021.
Decentralized Exchanges
Shortly after lending and borrowing platforms, decentralized exchanges (DEXs) were established. Instead of swapping cryptocurrencies through a centralized order book, DEXs allow users to swap cryptocurrencies against user-supplied liquidity pools. Liquidity-pool providers collect a share of all transaction fees, which are often far lower than traditional platforms. Exchanges are also completed instantly rather than waiting for another party to complete the other side of a transaction and investors can remain in control of funds at all times.
Stablecoins
Cryptocurrencies are one of the most volatile asset classes in the world, which isn’t great when you are trying to create a stable financial system. As a result, stablecoins were created. Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies that are pegged to a fiat currency and, therefore, provide shelter for those looking to avoid volatility.
Although these tokens are not a product of DeFi, the two go hand-in-hand. With the majority of stablecoins pegged to USD, these cryptocurrencies are heavily leveraged within DeFi applications. Stablecoins provide stability for the liquidity held within DeFi applications and provide a useful tool for the management of investors’ funds.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
As decentralized applications, it would be logical to question how development proposals are made. Within traditional finance, centralized entities steer native development. However, in DeFi, this development is led by DAOs.
DAOs are composed of a community of individuals that vote on and complete the administrative duties of DeFi applications. The rules for DAOs are embedded and executed by smart contracts, which means that they cannot be altered.
Derivatives & Synthetics Trading
Smart contracts and blockchain technology allow traditional assets to be tokenized. This includes bonds, commodities, indexes, and stocks. Derivates and synthetics within DeFi track the price on an underlying asset much the same as traditional finance. However, tokenized assets allow investors and traders to gain exposure to traditional assets without the need to use a centralized platform.
Insurance
Insurance is one of the largest sectors in the financial industry. It is now one of the major use cases within DeFi. All of the heavy paperwork in the current insurance system can be digitized through smart contracts. Although DeFi insurance is still in its infancy, there are several companies, including Nexus Mutual and Opyn that offer insurance against smart contract risks.
Gaming
Most new video games offer players the opportunity to buy in-game accessories. DeFi-integrated games take this idea one step further. Shortly after the overnight success of DeFi, video games began to integrate digital assets and leverage DeFi principles.
By integrating cryptocurrencies and DeFi mechanics, games can build internal economies. Games such as Axie Infinity and Star Atlas allow players to earn tokens from gameplay, purchase in-game characters, and trade accessories. With the incentives and rewards that DeFi brings, it will likely be heavily used in the gaming industry as we head into the future.
It is easy to see from the list above that DeFi has grown far beyond the realms of traditional finance. Thanks to its transparency and decentralized nature, it has managed to replicate and even enhance financial services.
Above all else, the DeFi sector has provided an ecosystem to utilize and leverage digital assets. Before DeFi, digital assets, such as BTC or ETH, were primarily used for transactions. However, just like physical assets, cryptocurrencies can now be leveraged in a variety of different ways.
As trustless, permissionless, and non-custodial, DeFi allows anyone to be their own bank. While technically you can do this in legacy finance, keeping gold or cash tucked under your bed at night is not that practical; it also means that you cannot leverage that wealth within other financial services. In comparison, DeFi allows you to retain control while enjoying the convenience of financial products.
New DeFi concepts
- Liquidity mining. Liquidity mining is a term used to refer to an investment strategy that involves lending cryptocurrencies to DeFi protocols. Cryptocurrency assets are then utilized by a DeFi product. In exchange for lending crypto and taking on the risk, liquidity providers are typically rewarded with a share of transaction fees or a share of native crypto tokens; or in some instances, both.
- Yield farming. Yield farming takes the process of liquidity mining one step further. Yield farming involves moving funds from one platform to the next in search of the best liquidity-mining returns. There are now DeFi platforms that are dedicated to helping investors find the best DeFi returns and automate the entire process.
- Wrapped cryptos. From DeFi the idea of transferring cryptocurrencies from a native blockchain to another blockchain was born. This involves “wrapping” a token so that it can be used within a new ecosystem. For example, investors can wrap Bitcoin to get wBTC. wBTC is an ERC-20 token, which is a type of token that can be used on the Ethereum blockchain. wBTC can then be used within DeFi applications in the Ethereum ecosystem.
- Oracles. Many smart contracts require real-world data to understand the outcome of an event. This is particularly important in prediction markets. For example, this may include the results of an election or the price movements of a real-world asset. Oracles deliver this real-world data to DeFi applications. Examples include Chainlink, Band Protocol, and API3.
- Flash loans. Developed within the DeFi sector, flash loans are uncollateralized loans that are borrowed and paid back within the same transaction. Sound confusing? Here’s how it works: Thanks to smart contracts, flash loans are a preprogrammed set of transactions. As funds can be accessed without collateral, flash loans are extremely useful for arbitrage opportunities. A user can borrow a loan, use that loan to generate profit, and return the loan within the same transaction. If the conditions of the loan are not met, the loan is returned so that it is like nothing ever happened. Although undoubtedly complicated, flash loans are another great example of the power of DeFi.
- Money legos. The final term that is native to the world of DeFi is the idea of “money legos.” Different DeFi applications are sometimes referred to as “legos”; a reference to toy Lego blocks. These toy blocks can be easily and conveniently snapped together. Thanks to the open-source and transparent nature of DeFi, many applications in the space can equally be snapped together like “money legos.” By snapping together money legos, brand-new products and services can be created.
What Are the Advantages of DeFi?
There is a reason why decentralized finance has exploded through 2020 and 2021. Although user-friendliness needs some work, those in the know have enjoyed the fair returns, transparent operations, open access, and control that DeFi has to offer.
- Fair returns. Centralized finance takes a share of all profits. Let’s use an example to illustrate. Investor A opens a savings account and gets a 1% interest rate on the funds deposited. The bank uses those funds to generate a 4% return. The bank takes 3% as profit and hands the remaining 1% to Investor A. In decentralized finance, Investor A would get the majority of the 4% interest return.
- Transparency. The transparency of DeFi is twofold. Firstly, as DeFi apps are built on top of blockchains, all transactions are recorded publicly. Although the majority of transactions can’t be undone and cannot be associated with a specific person, there are ways to view and follow the movement of funds. Secondly, the majority of DeFi apps post the underlying code for applications online. Otherwise known as open source, this allows the code to be verified. This greater level of transparency leads to a greater level of composability.
- Composability. With transparency, comes increased composability; which is just another way of saying integration. DeFi apps can work together in ways that centralized finance institutions could never achieve. As a result of joining these “money legos,” new and advanced financial products have been and will likely continue to be produced within the DeFi sector.
- Anonymity. When using DeFi applications, there is no need to disclose your identity. As long as there is a digital wallet connected and you have cryptocurrencies to play with, financial services can be accessed.
- Non-custodial. DeFi applications do not require users to deposit cryptocurrencies into a platform to use the products and services on offer. Users can keep funds within their own personal cryptocurrency wallet and still leverage the deals that are on offer.
- Non-stop. Thanks to relying on smart contracts and not relying on human interaction, DeFi applications can remain operational all of the time. If you want to exchange one token for another through a DEX at 3 in the morning, you can.
What Are the Risks of DeFi?
For all the advantages of DeFi, there are certainly a few risks that investors and crypto holders should be aware of. Due to the infancy of the sector, there are still issues with hacking attempts, speculation around regulations, and coding errors. It cannot yet offer the stability and comfort of the traditional financial sector.
- Hacks. Although the blockchain is nearly impossible to tamper with, vulnerabilities are consistently exploited within the code that underlies DeFi applications. These applications are still programmed and designed by humans, which means that, inevitably, mistakes happen. Unfortunately, these mistakes can sometimes be exploited by malicious third parties. According to Chainalysis 2022 Crime Report, 97% of all crypto thefts in Q1 2022 occurred in the DeFi sector.
- Lack of regulation. One of the reasons that DeFi has exploded so much is the lack of red tape holding back developers. However, lack of regulation and consumer protection also means that there are no fail safes in place if something goes wrong. All bank accounts within the U.S. are insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation for up to $250,000. In addition, banks must hold a certain amount of reserves in place to ensure stability. These rules do not exist in DeFi.
- Over-collateralization. Accessing the majority of services in DeFi requires a user to deposit collateral. However, DeFi products and services typically require collateral that is greater than the value of the loan. This protects the liquidity supplied by users to DeFi applications and ensures that the volatility of crypto prices does not lead to instant liquidations. While innovative, it does place a restriction on who can access some services.
- Accountability of private keys. One of the greatest risks with DeFi is the level of accountability it places on an individual. While it is powerful to be your own bank, you have to take on the responsibility that comes with it. Private keys, the long unique codes that are often simplified into a seed phrase, are incredibly important. These keys are what allow individuals to sign off on transactions. As a result, keys need to be kept secure and backed up. If a private key is lost, there is no way to bring it back.
What Is the Future of DeFi?
DeFi has already revolutionized the way individuals think about leveraging wealth. Not bad for an industry that has been around for less than a decade. But what could the future hold for this finance disruptor?
If we look at blockchain, in 2015 most organizations and financial institutions were skeptical to adopt the technology. In 2022, hundreds of banks worldwide are investing in the blockchain and cryptocurrency industry. DeFi likely faces a similar adoption scenario.
Not all DeFi innovations are good and many won’t survive. But, it would be foolish to think that there won’t be game-changing innovations that will be adopted into the traditional financial system.
At the World Economic Forum in 2021, Rune Christensen, a co-founder of the DeFi application MakerDAO, described what he believed the future of DeFi to look like.
“It doesn’t matter if you’re a hedge fund manager on Wall Street or if you’re one of the 1.7 billion people that don’t even have a bank account. With DeFi, you have complete access. It’s not like trying to reinvent banks from scratch or trying to replace the financial system. It [DeFi] is just trying to replace a specific piece of it, which is the piece that basically works the worst right now.”
Some believe that in the future, DeFi will overthrow the traditional financial system and become the dominant method for accessing financial products. Perhaps it will be. But with the amount of control that traditional finance has, it is an unlikely scenario. In reality, it is more likely that DeFi will work in parallel with traditional finance, complementing the system that already exists.
Summary
The idea of DeFi is an extremely powerful one. It completely removes the shackles of the financial services provided by institutions and central banks. It is, therefore, likely one of the greatest steps ever towards an open and transparent financial system.
Is it worth putting all of your funds in the sector? Absolutely not. DeFi is still in its infancy and is certainly not without its risks. The level of financial accountability that comes with interacting with DeFi is also not for the faint-hearted. However, for those that are comfortable with the level of control it offers, the products and services that could stem from this sector of the cryptocurrency industry are truly limitless.




